Nuorten kanssa tehty uusi katutaideteos koristaa hoivakodin seinää
13.6.2025

Reimari on alle 30-vuotiaille nuorille suunnattu palvelu, joka tarjoaa tietoa, neuvontaa ja ohjausta erilaisiin elämäntilanteisiin ja kysymyksiin. Reimari järjestää myös maksuttomia tilaisuuksia, työpajoja ja kerhoja, jotka vastaavat nuorten toiveita ja tarpeita.
Oikopolut sisältöön
Tietoa nuorille Hobbybook Palvelun esittely Nuorisopalvelut Etsivä nuorisotyö Ohjaamo VaasaSivuiltamme löydät tietoa Reimarin tieto-, neuvonta- ja ohjauspalveluista sekä ryhmätoiminnasta. Löydät myös kattavasti infoa Vaasan alueen muista palveluista, sekä hyödyllistä ja mielenkiintoista tietoa nuorten arkeen ja elämään liittyvistä asioista.

Meiltä saat apua esimerkiksi kesätyön hakuun, CV:n laatimiseen, harrastusvaihtoehtojen löytämiseen sekä muihin nuorten elämää koskeviin asioihin. Olipa kyseessä sitten pieni kysymys tai suurempi haaste, voit kääntyä puoleemme – tule käymään tai aloita vaikkapa chat kanssamme!
Lue lisää
Reimari tarjoaa alle 30-vuotiaille nuorille monipuolista harrastustoimintaa, työpajoja ja tilaisuuksia, joissa voit kokeilla uusia taitoja ja löytää inspiraatiota.
Lue lisääArtikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset
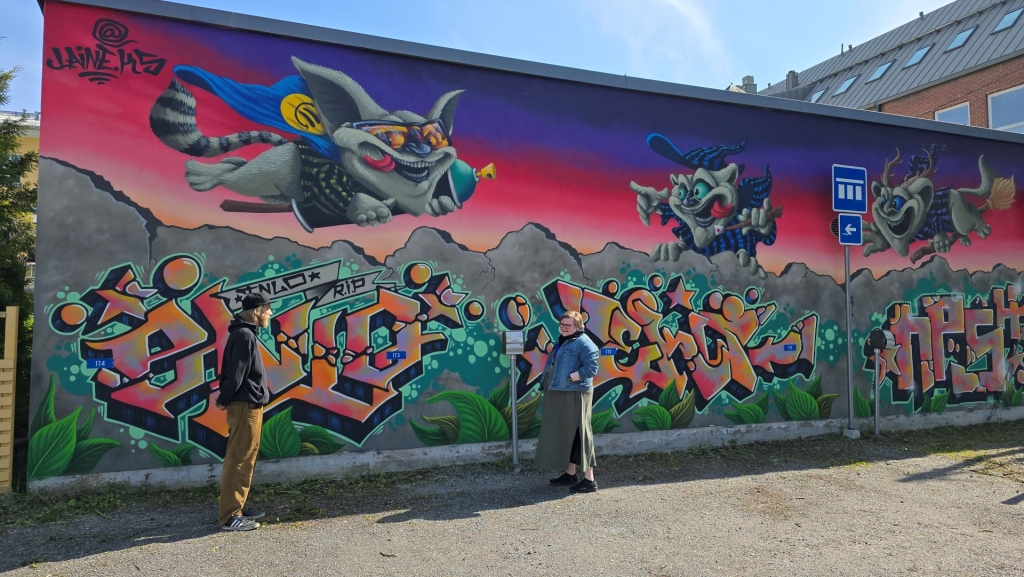

Artikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset
Artikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset

Artikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset

Artikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset

Artikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset

Artikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset

Artikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset

Artikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset

Artikkelin kategoriat: Uutiset

ma–to klo 10.00–16.00
pe klo 10.00–15.00
ma–pe klo 10.00–15.00
Mikäli emme ole paikalla kysymystä jättäessäsi, jätäthän chattiin sähköpostiosoitteesi, jotta voimme vastata viestiisi Reimarin aukioloaikojen puitteissa.
Nuorisotiedottaja , Nuorisopalvelut
+358400872288
Harrastuskoordinaattori , Nuorisopalvelut
+358404839032
Ilmoitukset